How can I easily wire my IP throughout hierarchy in RTL flow?
(This article applies to RTL flow, with VHDL)
When using the ‘RTL’ flow, EXOSTIV IP is generated as a synthesized module that is inserted ‘manually’ into the RTL (VHDL/Verilog) source code. As opposed to the netlist flow, the RTL flow uses a semi-automatic insertion process.
EXOSTIV IP insertion requires:
1) Creating an instance of EXOSTIV IP in the RTL code
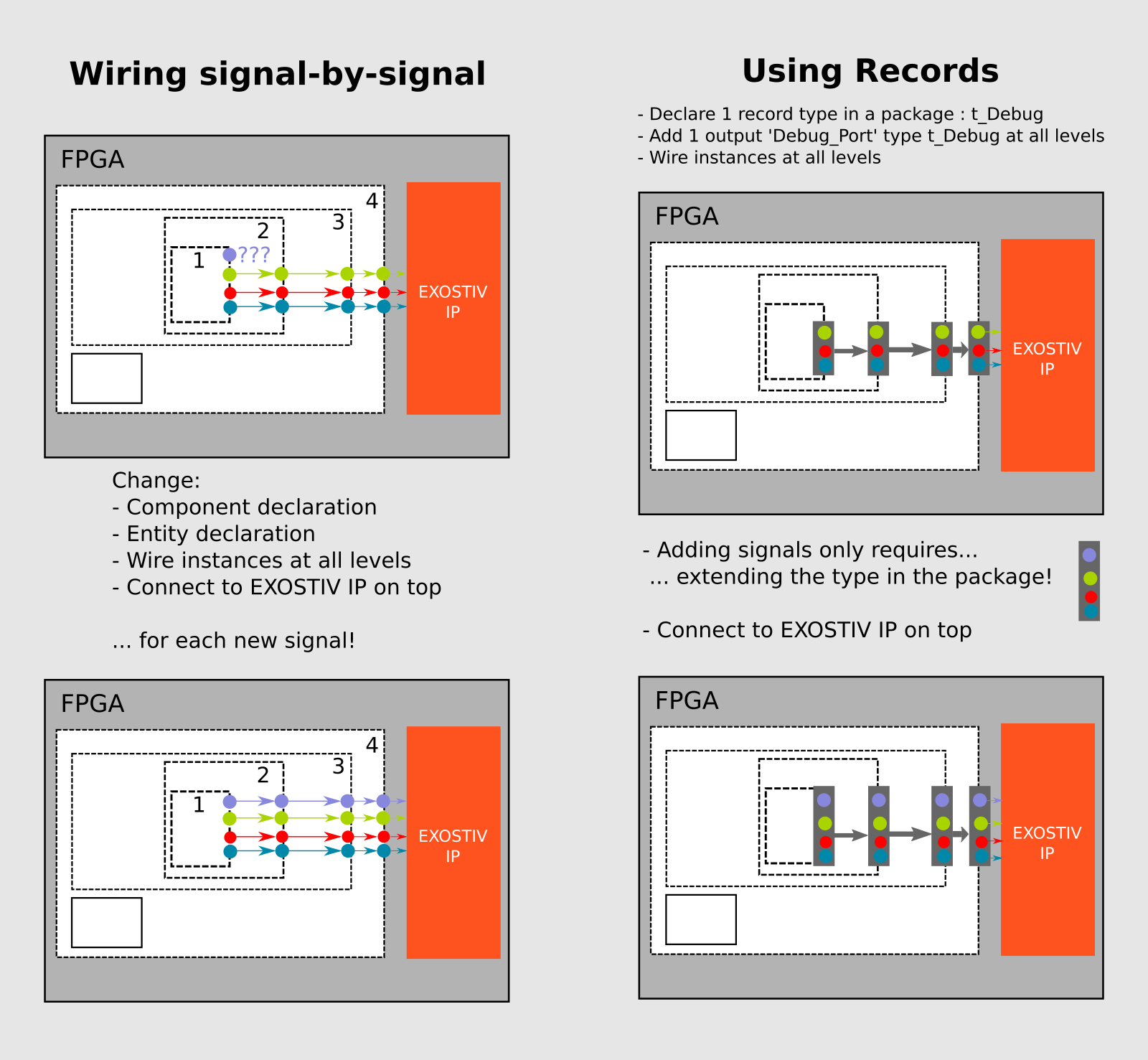
2) ‘Wiring’ the logic signals to be observed to EXOSTIV IP
3) Connecting the clocks, I/Os, …
Step 2 above – the wiring of the signals that have to be observed – can be a difficult task, especially when a large number of nodes must be connected to the EXOSTIV IP instance throughout the design hierarchy.
In VHDL, a faster way to connect nodes throughout hierarchy uses records at the interface of all the modules.
The principles are:
– A debug type t_Debug, based on ‘records’ is defined in a central package.
– A port with type t_Debug is added to modules throughout the code hierarchy.
– This work requires modifying the component and entity declarations for all the modules subject to observation with EXOSTIV.
– The debug ports are connected up to the top level.
As opposed to wiring of signals separately, this work will be done only once.
==> From there, wiring an additional signal up to the top level only requires modifying the record type in the VHDL package.